You are here: Home » Classification by Functions » Intellectual Property » Get to Know Intellectual Property 

Get to Know Intellectual Property
| Intellectual Property | ||
| Trademarks | ||
| Patents | ||
| Copyright |
| Intellectual Property |
- What is Intellectual Property?
Intellectual property is the property generated in the process of intellectual activities. It can be possessed and used, and generated benefits. Similar to tangible property (e.g. house and car), intellectual property which is an intangible property is also protected by the law. The major components of intellectual property include copyrights, patents, trademarks, etc.
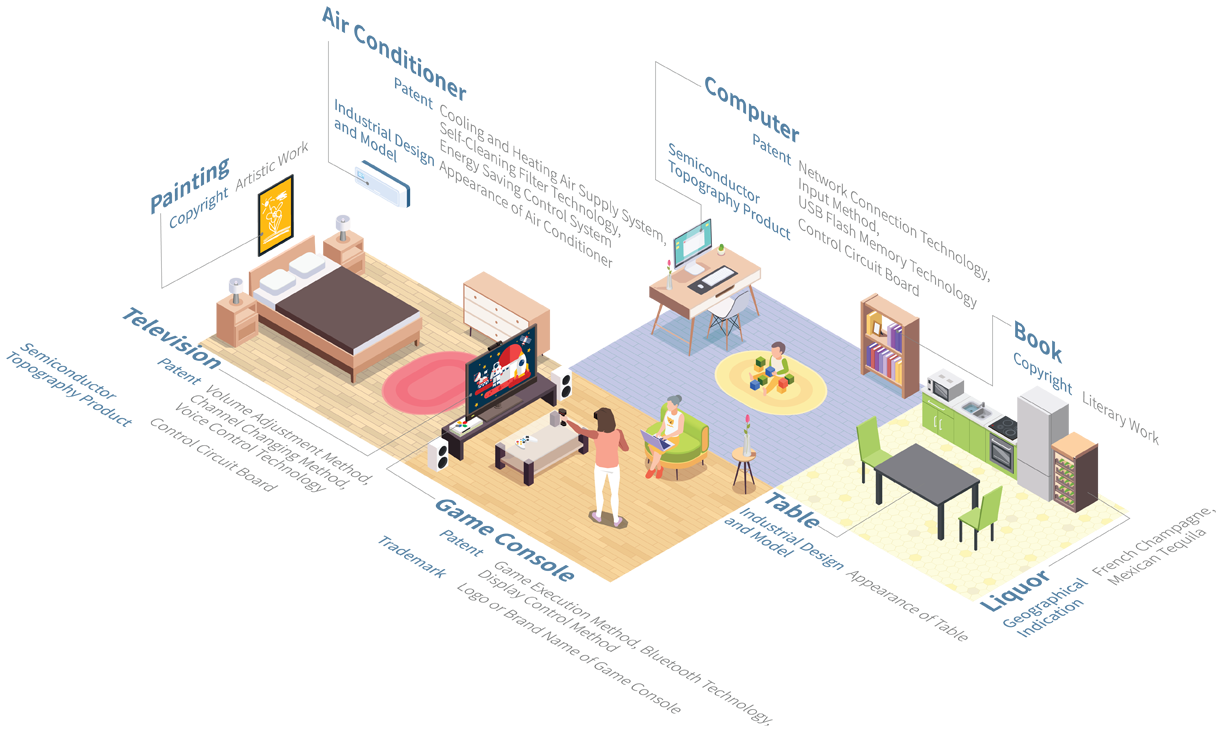
Intellectual property is strongly related to our daily lives, such as articles in newspapers/magazines, TV/radio programmes, songs, movies, paintings, sculptures, phones, audio equipment, vehicles, fashion design, and brand-names logos on sport equipment.
- Example of Intellectual Property:
- Why does Intellectual Property need to be protected?
Protection of intellectual property protects the results of intellectual activities of mankind. It ensures the efforts of creator/inventor can be rewarded. Therefore, this encourages creator/inventor to continue their creative works, which improves production efficiency and our living standards. It also motivates economic development.
Since there are more business opportunities in the Macao SAR, protection of intellectual property has become very important, especially to investors. This is because protection of intellectual property helps companies to become competitive and stimulates economic growth.
- What is protected in Intellectual Property Rights?
Intellectual property rights protect the results of intellectual activities of mankind. It gives the owner of intellectual property exclusive rights of possession and use of the creation or invention. Therefore owner’s rights can be protected. They also help to provide a fair environment for business.
Protected aspects include: copyrights, invention patents, utility patents, industrial models and designs, trademarks, topographies of semiconductor products, names and emblems of establishments, designation of origin and geographic indications, and awards.
| Trademarks |
- What is Trademark?
A trademark is a sign that is used to distinguish the goods or services of a company from those of others.
The sign of a trademark can be words, characters, numbers, figurative elements, combinations of different colors, or any combination of these. Also, it can be three-dimensional, such as a container of goods and the shape of the packaging of goods. Moreover, it can be sounds as well.
- How can we distinguish “trademark” and “industrial model and design”?
A trademark is a sign that is used to distinguish the goods or services of a company from those of others. Generally, the sign is formed by words, figures, symbols or other combinations.
Protection of industrial models and designs means protection of the whole or partial appearance of goods. It is formed by shapes, figurative elements, colors or any combination of these.
The common features of “trademark” and “industrial model and design” are that both of them possess shapes and figurative elements. The major difference is that industrial models and designs require the good itself as the protected subject, but trademark does not.
| Patents |
- What is patent?
A patent gives the exclusive right to the owner of an invention to exploit the invention for a limited period. To obtain a patent, the applicant needs to submit an application according to the relevant administrative procedures. A patent will then be granted subject to approval further to examination.
A patent is a component of intellectual property and a kind of intangible property. Similar to tangible property, a patent can be succeeded or transferred during its period of validity.
- What is protected under a registered patent?
The owner of a patent has the exclusive rights to manufacture, use, sell, perform “offering for sale” and import the products under the patent, or use the methods covered by the patent. The owner also has the right to prohibit other companies or persons from using the products or methods under the patent.
Any person who uses products or methods under a patent must obtain a license from the owner and pay the owner. Otherwise, such usage may be liable of patent infringement.
- What are the types of patents?
A patent can be classified into three major types: invention patent, utility patent and industrial model and design.
An invention patent refers to new technical schemes for products, methods or improvement to existing technologies.
A utility patent refers to new technical schemes for shape, structure or their combinations of a product.
An industrial model & design refers to the protection of the shape, pattern, color or their combinations applied on a new design of a product, which is aesthetic and capable of being applied on an industrial scale.
- What are the differences between invention patent, utility patent and industrial model & design?
Invention patents and utility patents focus on the improvement of the function, technology adopted, manufacturing technique, users’ convenience, etc. of a product. However, the technical level of a utility patent is lower than that for invention patent.
Industrial model & design refers to the protection of shape, pattern, color or their combinations applied on a new design of a product, which is aesthetic and capable of being applied on a industrial scale.
Therefore, industrial model & design are obviously different from the invention and utility patents, especially because the former focus on aestheticism and art in the design that can increase the competitiveness of a product in the market.
- How to calculate the durations of protection of registered invention patent, utility patent and industrial model & design?
For registered invention patents (or applied by extension), the duration of protection is 20 years, counting from the date of application (or the date of application in China).
For registered utility patents, the duration of protection is 10 years, counting from the date of application.
For registered industrial models & designs, the duration of protection is 25 years, counting from the date of application.
- What kind of technologies can only be applied for invention patents, but not utility patents?
The targets of protection of invention and utility patents are different. In comparative terms, the target scope of protection of invention patents is wider than that for utility patents: methods, substance (no specific form), biomaterials and the application thereof only apply for invention patents. Products (with a specific form) can apply for invention patents and/or utility patents. If a person applies both types of patents at the same time, only an invention patent or a utility patent will be granted.
- Why does discovery not classify as invention patent?
Discovery does not comply with the definition of invention or creation because it does not contain creative elements. Examples include the discovery of a substance, phenomenon, conversion process, property and rule. Therefore, a patent will not be granted for a discovery.
- What are industrial models & designs?
Industrial models & designs refer the protection of the shape, pattern, color or their combinations applied for a new design of a product, which is aesthetic and capable of being industrial applied.
- Are the colors of registered “industrial models & designs” protected?
In registered industrial models & designs, colors of the product or decoration are protected. Whenever an industrial model & design contains colors, the applicant should claim the right of using the colors and attach them with relevant figures or photos that show the colors in the application.
- What designs are not eligible for registration?
Examples of designs which are not eligible for registration include: (1) designs which only serve specified function(s), e.g. an USB plug; (2) designs of a component which cannot use or form a product by itself, or that can combine with other products after combination of its own type of components, and possess specified shape and size, e.g. a piece of puzzle.
| Copyright |
- What is copyright?
Copyright refers to the creator’s right to possess, use, and generate benefits from his pieces.
- What is protected by copyright?
Any pieces which are the product of human creativity are protected by copyright, e.g. literary works, artistic works, movies, musical works, dramatic works, computer software, photography, sculpture, ceramic pieces, architecture, etc.
- What are the related rights of copyright?
Related rights of copyright refer to the formats of books and periodicals designed by the publisher, performances of performers, audio and video products of the producer, the programme produced by radio stations and TV stations.
- What is not protected by copyright?
Items which are not protected by copyright include (but not limited to them) are: idea, program, organization, operating method, rule, concept, principle, discovery, not written or recorded piece, piece which is not written by original author, information for public use, daily news, article which only reports incidents, speech given in a form of discussion for the benefit of the community, political speeches, official pieces, laws and regulations and their translations.
- A student writes a computer program according to the idea, direction and recommendation of his teacher. Whom shall the copyright belong to?
Ideas and directions are not protected by copyright. Although the teacher has given his idea, directions and recommendations, the student has designed the program on his own. The student’s work is the result of his creative activities, therefore the copyright shall belong to him.
- How to obtain copyright protection?
A creator can enjoy copyright protection without registration. In fact, the protection is effective automatically once the piece is made, no matter if it is disclosed or not. Copyright only protects the form or format of a piece, but not the idea, method, opinion and fact.
- Can a copyright be co-owned?
Yes. Copyright of a piece, which is created by a team, is co-owned by all the team members.
- How long does a copyright last for?
In general, a copyright lasts from the date it was acquired until 50 years after the creator’s death.
For co-owned copyright, it lasts from the date it was acquired until 50 years after the deaths of all the creators.
For the copyright of anonymous piece, published or disclosed piece without the indication of true identity of the creator, it lasts from the date it was acquired until 50 years after publication of the piece. If the parts, chapters or sections of a piece are not published or publicized at the same time, the effective periods of each parts, chapters or sections will be calculated separately.
- How to register as an organization of collective administration of copyright?
According to article 196 of the “Copyright and Related Rights Code” approved by the Decree-law no. 43/99/M (amended by Law no. 5/2012 of April 10), the applicant should complete the ”著作權及相關權利集體管理機構登記申請書 / Pedido de Registo dos Organismos de Gestão Colectiva de Direitos de Autor e de Direitos Conexos” (Application Form for the Registration of the Collective Management Agencies of Copyright and Related Rights), accompanied by relevant documents, and submit the application to the Economic and Technological Development Bureau at least 30 days before the commencement of operation of the organization.
For details, please refer to “Intellectual Property – Administrative Procedures” in the website of Economic and Technological Development Bureau.
Note: The above information can be used as reference only, but not legal advice. Before taking the actions mentioned above, please seek professional advice first.

